System Capacity
Strategy
Build capacity of Substance Abuse Connect (SAC) to sustain progress.
Activities List
“A coalition that creates a safe space to have hard conversation” Kristin Lundgren
Models/Frameworks
“Collective impact” describes an intentional way of working together and sharing information for the purpose of solving a complex problem. Proponents of collective impact believe that the approach is more likely to solve complex problems than if a single nonprofit were to approach the same problem(s) on its own. While collective impact seems very similar to plain old “collaboration,” there are certain characteristics that distinguish collective impact initiatives – and make them successful.
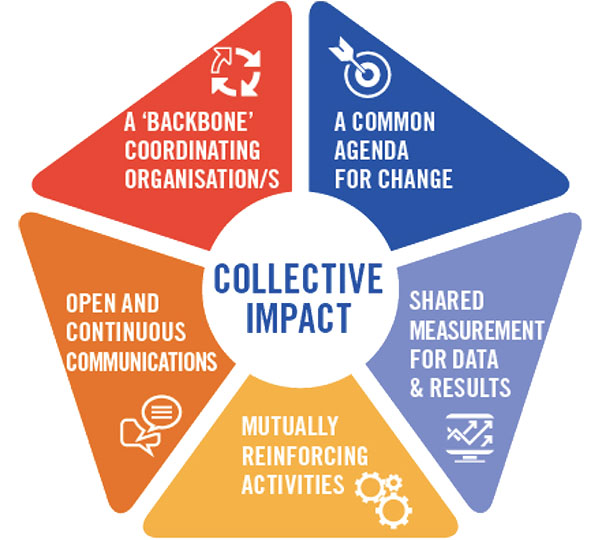
Collective Impact Framework
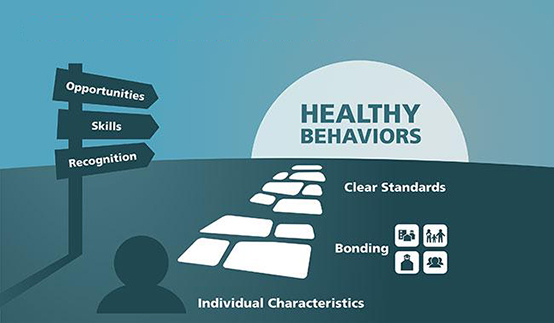
Communities That Care
Models/Frameworks
Communities That Care is a science-based public health approach proven to promote healthy youth development and reduce youth health and behavior problems community wide. Communities That Care employs the Social Development Strategy to foster young people’s wellbeing through opportunities, skill-building and recognition. In this way, protective factors are strengthened and risk factors are reduced, resulting in healthier kids, families and communities. A rigorous scientific trial of the Communities That Care model demonstrated reductions in rates of youth violence, crime and substance use.
Diversion and Treatment
Strategy
Increase capacity of crisis support and criminal justice system to effectively prevent and / or manage drug-related crisis with the intention of jail diversion and prevention of recidivism
Models/Frameworks
“Behavioral health crises are complex situations that often involve the coordination of several systems, including physical and behavioral healthcare, law enforcement, emergency medical services, and social service programs. A successful behavioral health crisis system leverages all available community resources to mitigate gaps in care and increase communication and collaboration amongst stakeholders to secure the best outcomes for community members.”
SAMHSA Continuum of Care for Crisis Mitigation and Management
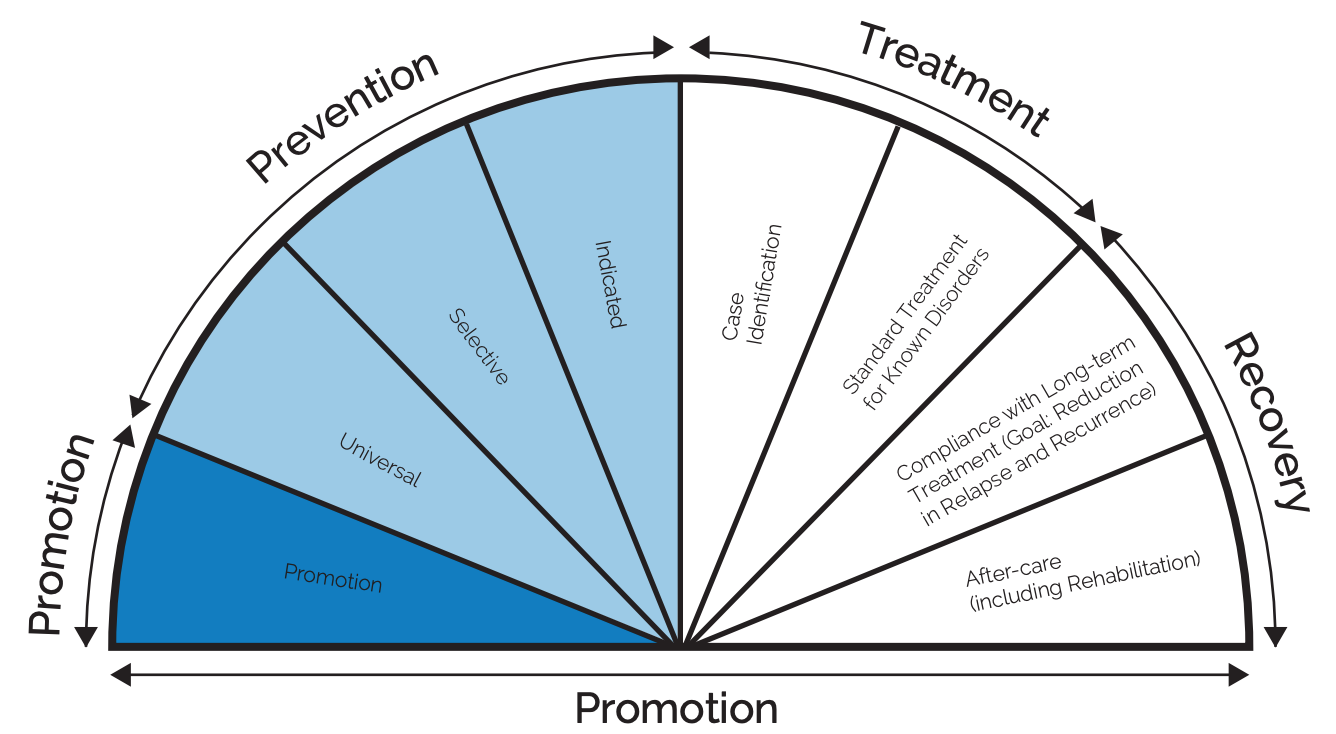
Graphic for Structure/ Flow Chart
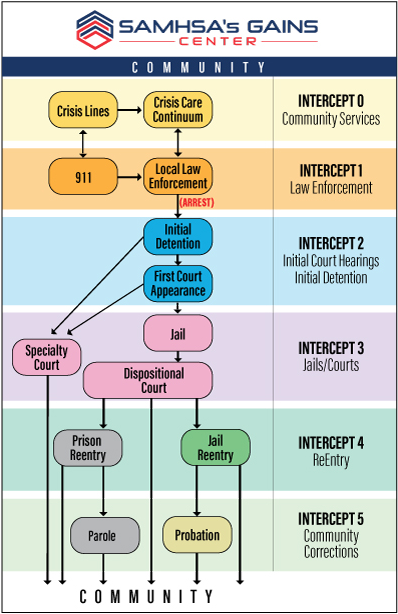
SIM Sequential Intercept Model
The SIM helps communities identify resources and gaps in services at each intercept and develop local strategic action plans. The SIM mapping process brings together leaders and different agencies and systems to work together to identify strategies to divert people with mental and substance use disorders away from the justice system into treatment.
- Plot resources and gaps across the SIM.
- Identify local behavioral health services to support diversion from the justice system.
- Introduce community system leaders and staff to evidence-based practices and emerging best practices related to each intercept.
- Enhance relationships across systems and agencies.
- Create a customized, local map and action plan to address identified gaps.
Prevention
Strategy
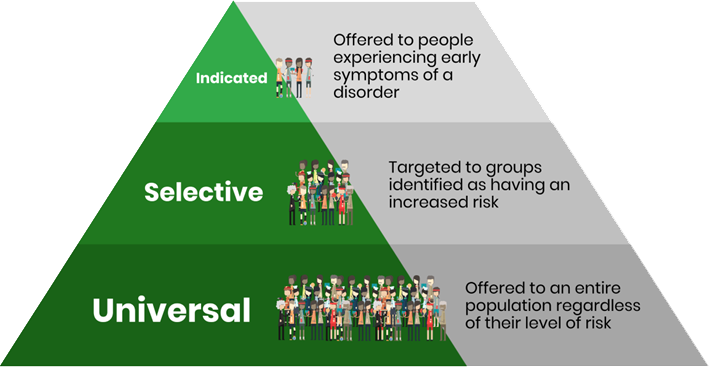
Use universal, selected, and targeted approaches to increase protective factors and decrease risk factors.
Models/Frameworks
CSAP Strategies
The Center for Substance Abuse Prevention (CSAP) works with federal, state, public, and private organizations to develop comprehensive prevention systems by:
- Providing national leadership in the development of policies, programs, and services to prevent the onset of illegal drug use, prescription drug misuse and abuse, alcohol misuse and abuse, and underage alcohol and tobacco use
- Promoting effective substance abuse prevention practices that enable states, communities, and other organizations to apply prevention knowledge effectively
As a result of its efforts, CSAP’s work creates:
- Supportive workplaces, schools, and communities
- Drug-free and crime-free neighborhoods
- Positive connections with friends and family

Strategic Prevention Framework
Strategy
Use universal, selected, and targeted approaches to increase protective factors and decrease risk factors.
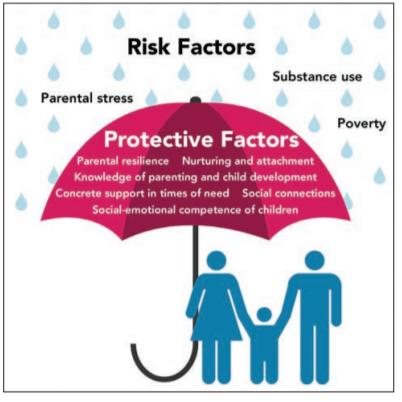
Risk and Protective factors
Prevention science has identified biological, psychological, family, community, and cultural characteristics that are associated with a higher likelihood of an individual developing a substance abuse or related behavioral health problem, these are known as risk factors. There are also factors at the individual, family, and community levels proven to reduce the likelihood of developing a substance abuse or behavioral health problem, called protective factors. Effective Prevention focuses on strengthening protective factors and reducing risk factors in multiple contexts.
Evidence Based Prevention
As Prevention has evolved over time, interventions have been evaluated to measure impact and overall effectiveness. A prevention program or intervention is considered evidence-based if there is demonstrated evidence of effectiveness under a set of defined conditions. When selecting an intervention, evidence is evaluated, and priority is given to those programs with strong evidence of effectiveness.
Action Committees List
Prenatal
support pregnant and postpartum women at-risk for or engaged in substance misuse.
Youth/Schools
identifying, supporting, educating, and referring students age K to early adulthood (includes in and out of school)
Parents/Caregivers
empowering via education and access to information/resources
Business
providing resources and education to employers to support at-risk employees
Communications
dissemination of information to all ages through universal, selected and targeted approaches using varying medium
Prevention Policies
advocating for prevention at the community and state levels
